DBCC SHOW_STATISTICS displays current query optimization statistics for a table or indexed view. The query optimizer uses statistics to estimate the cardinality or number of rows in the query result, which enables the query optimizer to create a high quality query plan. For example, the query optimizer could use cardinality estimates to choose the index seek operator instead of the index scan operator in the query plan, improving query performance by avoiding a resource-intensive index scan.
The query optimizer stores statistics for a table or indexed view in a statistics object. For a table, the statistics object is created on either an index or a list of table columns. The statistics object includes a header with metadata about the statistics, a histogram with the distribution of values in the first key column of the statistics object, and a density vector to measure cross-column correlation. The Database Engine can compute cardinality estimates with any of the data in the statistics object.
DBCC SHOW_STATISTICS displays the header, histogram, and density vector based on data stored in the statistics object. The syntax lets you specify a table or indexed view along with a target index name, statistics name, or column name. This topic describes how to display the statistics and how to understand the displayed results.
For more information, see Statistics.
Syntax
-- Syntax for SQL Server and Azure SQL Database
DBCC SHOW_STATISTICS ( table_or_indexed_view_name , target )
[ WITH [ NO_INFOMSGS ] < option > [ , n ] ]
< option > :: =
STAT_HEADER | DENSITY_VECTOR | HISTOGRAM | STATS_STREAM
-- Syntax for Azure SQL Data Warehouse and Parallel Data Warehouse
DBCC SHOW_STATISTICS ( table_name , target )
[ WITH {STAT_HEADER | DENSITY_VECTOR | HISTOGRAM } [ ,...n ] ]
[;]
Arguments
table_or_indexed_view_name
Name of the table or indexed view for which to display statistics information.
Name of the table or indexed view for which to display statistics information.
table_name
Name of the table that contains the statistics to display. The table cannot be an external table.
Name of the table that contains the statistics to display. The table cannot be an external table.
target
Name of the index, statistics, or column for which to display statistics information. target is enclosed in brackets, single quotes, double quotes, or no quotes. If target is a name of an existing index or statistics on a table or indexed view, the statistics information about this target is returned. If target is the name of an existing column, and an automatically created statistics on this column exists, information about that auto-created statistic is returned. If an automatically created statistic does not exist for a column target, error message 2767 is returned.
In SQL Data Warehouse and Parallel Data Warehouse, target cannot be a column name.
Name of the index, statistics, or column for which to display statistics information. target is enclosed in brackets, single quotes, double quotes, or no quotes. If target is a name of an existing index or statistics on a table or indexed view, the statistics information about this target is returned. If target is the name of an existing column, and an automatically created statistics on this column exists, information about that auto-created statistic is returned. If an automatically created statistic does not exist for a column target, error message 2767 is returned.
In SQL Data Warehouse and Parallel Data Warehouse, target cannot be a column name.
NO_INFOMSGS
Suppresses all informational messages that have severity levels from 0 through 10.
Suppresses all informational messages that have severity levels from 0 through 10.
STAT_HEADER | DENSITY_VECTOR | HISTOGRAM | STATS_STREAM [ ,n ]
Specifying one or more of these options limits the result sets returned by the statement to the specified option or options. If no options are specified, all statistics information is returned.
Specifying one or more of these options limits the result sets returned by the statement to the specified option or options. If no options are specified, all statistics information is returned.
STATS_STREAM is Identified for informational purposes only. Not supported. Future compatibility is not guaranteed.
Result Sets
The following table describes the columns returned in the result set when STAT_HEADER is specified.
The following table describes the columns returned in the result set when DENSITY_VECTOR is specified.
The following table describes the columns returned in the result set when the HISTOGRAM option is specified.
Remarks
Statistics update date is stored in the statistics blob object together with the histogram and density vector, not in the metadata. When no data is read to generate statistics data, the statistics blob is not created, the date is not available, and the updated column is NULL. This is the case for filtered statistics for which the predicate does not return any rows, or for new empty tables.
Histogram
A histogram measures the frequency of occurrence for each distinct value in a data set. The query optimizer computes a histogram on the column values in the first key column of the statistics object, selecting the column values by statistically sampling the rows or by performing a full scan of all rows in the table or view. If the histogram is created from a sampled set of rows, the stored totals for number of rows and number of distinct values are estimates and do not need to be whole integers.
To create the histogram, the query optimizer sorts the column values, computes the number of values that match each distinct column value and then aggregates the column values into a maximum of 200 contiguous histogram steps. Each step includes a range of column values followed by an upper bound column value. The range includes all possible column values between boundary values, excluding the boundary values themselves. The lowest of the sorted column values is the upper boundary value for the first histogram step.
The following diagram shows a histogram with six steps. The area to the left of the first upper boundary value is the first step.
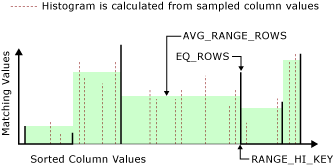
For each histogram step:
- Bold line represents the upper boundary value (RANGE_HI_KEY) and the number of times it occurs (EQ_ROWS)
- Solid area left of RANGE_HI_KEY represents the range of column values and the average number of times each column value occurs (AVG_RANGE_ROWS). The AVG_RANGE_ROWS for the first histogram step is always 0.
- Dotted lines represent the sampled values used to estimate total number of distinct values in the range (DISTINCT_RANGE_ROWS) and total number of values in the range (RANGE_ROWS). The query optimizer uses RANGE_ROWS and DISTINCT_RANGE_ROWS to compute AVG_RANGE_ROWS and does not store the sampled values.
The query optimizer defines the histogram steps according to their statistical significance. It uses a maximum difference algorithm to minimize the number of steps in the histogram while maximizing the difference between the boundary values. The maximum number of steps is 200. The number of histogram steps can be fewer than the number of distinct values, even for columns with fewer than 200 boundary points. For example, a column with 100 distinct values can have a histogram with fewer than 100 boundary points.
Density Vector
The query optimizer uses densities to enhance cardinality estimates for queries that return multiple columns from the same table or indexed view. The density vector contains one density for each prefix of columns in the statistics object. For example, if a statistics object has the key columns
CustomerId, ItemId and Price, density is calculated on each of the following column prefixes.Restrictions
DBCC SHOW_STATISTICS does not provide statistics for spatial or xVelocity memory optimized columnstore indexes.
Permissions for SQL Server and SQL Database
In order to view the statistics object, the user must own the table or the user must be a member of the
sysadmin fixed server role, the db_owner fixed database role, or the db_ddladmin fixed database role.
SQL Server 2012 (11.x) SP1 modifies the permission restrictions and allows users with SELECT permission to use this command. Note that the following requirements exist for SELECT permissions to be sufficient to run the command:
- Users must have permissions on all columns in the statistics object
- Users must have permission on all columns in a filter condition (if one exists)
- The table cannot have a row-level security policy.
To disable this behavior, use traceflag 9485.
Permissions for SQL Data Warehouse and Parallel Data Warehouse
DBCC SHOW_STATISTICS requires SELECT permission on the table or membership in one of the following:
- sysadmin fixed server role
- db_owner fixed database role
- db_ddladmin fixed database role
Limitations and Restrictions for SQL Data Warehouse and Parallel Data Warehouse
DBCC SHOW_STATISTICS shows statistics stored in the Shell database at the Control node level. It does not show statistics that are auto-created by SQL Server on the Compute nodes.
DBCC SHOW_STATISTICS is not supported on external tables.
Examples: SQL Server and SQL Database
A. Returning all statistics information
The following example displays all statistics information for the
AK_Address_rowguid index of the Person.Address table in the AdventureWorks2012 database.
SQL
DBCC SHOW_STATISTICS ("Person.Address", AK_Address_rowguid);
GO
B. Specifying the HISTOGRAM option
This limits the statistics information displayed for Customer_LastName to the HISTOGRAM data.
SQL
DBCC SHOW_STATISTICS ("dbo.DimCustomer",Customer_LastName) WITH HISTOGRAM;
GO
Examples: SQL Data Warehouse and Parallel Data Warehouse
C. Display the contents of one statistics object
The following example displays the contents of the Customer_LastName statistics on the DimCustomer table.
SQL
-- Uses AdventureWorks
--First, create a statistics object
CREATE STATISTICS Customer_LastName
ON AdventureWorksPDW2012.dbo.DimCustomer (LastName);
GO
DBCC SHOW_STATISTICS ("dbo.DimCustomer",Customer_LastName);
GO
The results show the header, the density vector, and part of the histogram.


No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.